Marketing Plan Template
Download Marketing Plan Template
Word | PDF | Google Doc | Smartsheet
A marketing plan is a high-level document that guides your strategic initiatives and ensures your marketing goals are aligned with your overall business objectives. Use this pre-built marketing plan template to outline the purpose your business serves, as well as its strategic goals, target market, and standards of performance, to ensure you have a thorough and deliberate plan of action.
One-Page Marketing Plan Template
Download One-Page Marketing Plan Template
Excel | Word | PDF | Google Doc | Smartsheet
This customizable one-page marketing plan takes the comprehensiveness of a formal marketing plan and pares it down to the key elements for easy scannability. This template has space for a concise business summary, overall objectives, target market, marketing strategy, financial requirements, and more. It also contains an action plan to detail marketing activities, role assignments, deadlines, and costs.
Business Marketing Plan Template
Download Business Marketing Plan Template
Word | PDF | Smartsheet
This template takes all of the essential elements of a marketing plan and organizes them into sections, but you can also add and remove components of the plan according to your needs. Use this customizable template to write your executive summary, mission and vision statements, marketing strategy, core capabilities, main goals, budget, and more, with an appendix included to back up your research and findings.
Small Business Marketing Plan Template
Download Small Business Marketing Plan Template
Word | PDF | Smartsheet
A small business marketing plan can be simple or elaborate, depending on your needs and the nature of your organization. This marketing plan template is fully customizable, and will guide your small business in the identification and description of your project, the mission and vision of your company, the problem you are solving, short and long-term marketing goals, the 4Ps of your marketing mix, marketing channel strategy, and more.
Marketing Plan Template for Startup Business
Download Marketing Plan Template for Startups
This pre-built marketing plan template for startups provides the savvy entrepreneur with a strong foundation from which to build his or her marketing strategies. This template will help you develop clear short and long-term business goals, identify your target market, learn your buyer’s buying cycle, pinpoint your unique selling proposition (USP), track standards of performance and measurement methods, and more, so you can feel confident in a solid plan of action.
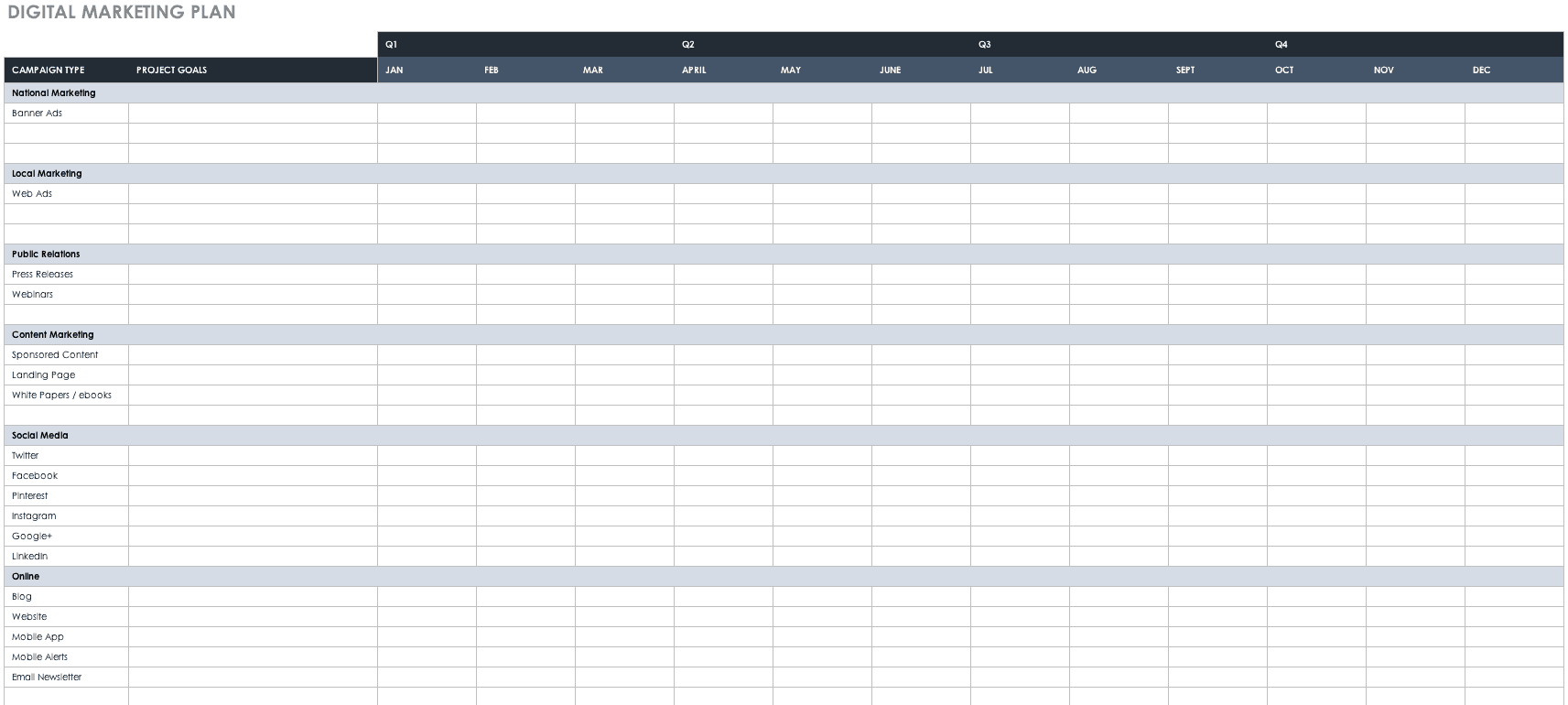
Digital Marketing Plan Template
Digital Digital Marketing Plan Template
This digital marketing plan template includes sections for online advertising and analytics, content marketing and SEO strategy, social media, and tools for tracking metrics. The template is divided into months, so you can create a timeline for your digital marketing plan. Use this template to create a comprehensive plan of action for online marketing.
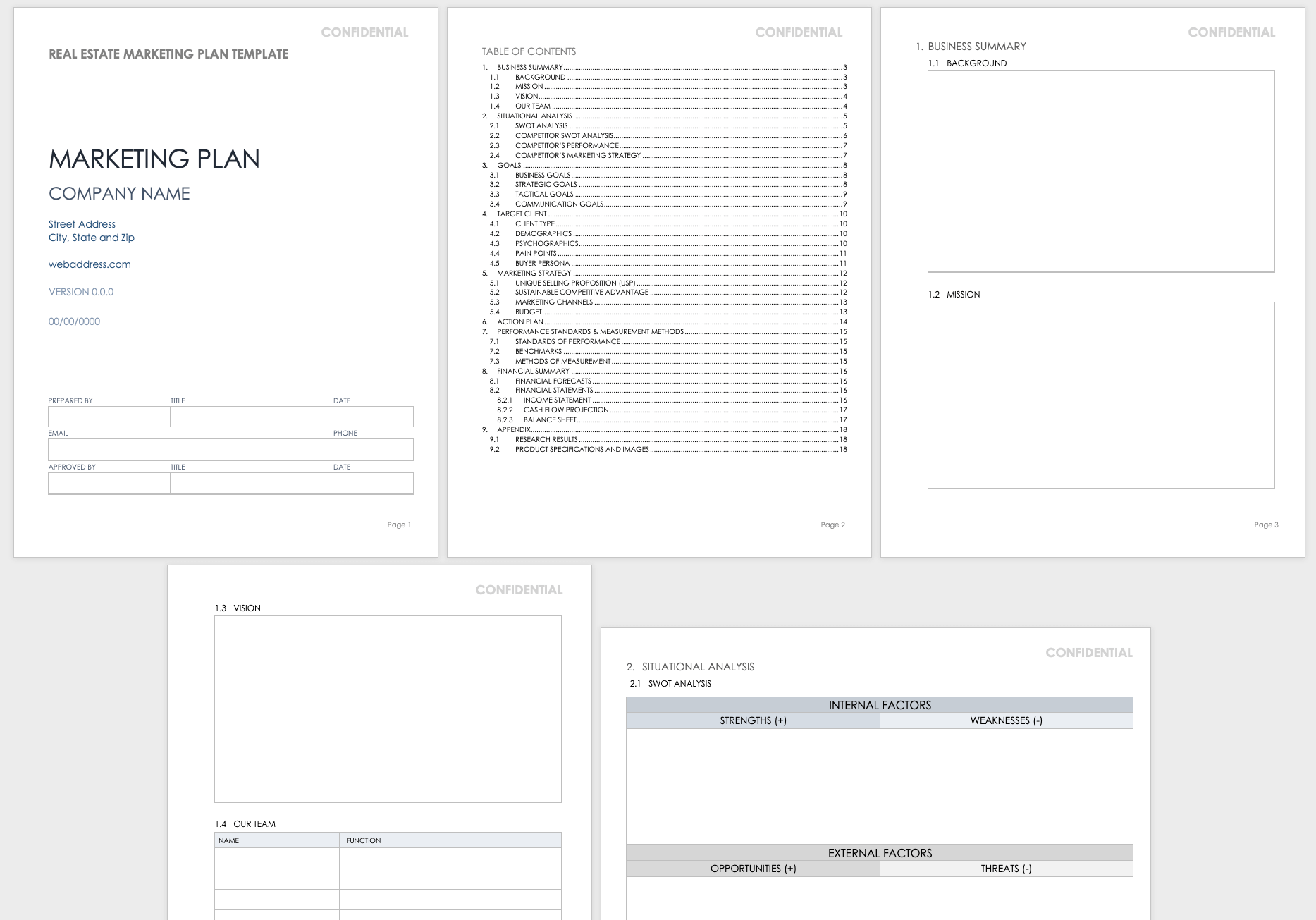
Real Estate Marketing Plan Template
Download Real Estate Marketing Plan Template
This pre-built real estate marketing plan template is customizable, and comes ready to outline your strategic and tactical goals, conduct a SWOT analysis (including a competitor SWOT analysis), identify your target client type (e.g. first-time buyer, home seller, renter, etc.), define your marketing channels, provide financial forecasts, and more. It also includes a built-in plan of action for you to plan activities, assign roles, and set projected dates.
Marketing Plan Template for Nonprofit
Download Nonprofit Marketing Plan Template
This marketing plan template is tailored to meet the unique requirements of a nonprofit business. Use this customizable template to detail the organization’s background, funding climate, a comparative analysis of competitors, profile of stakeholders, short and long-term marketing goals, positioning statement, financial requirements, and more.
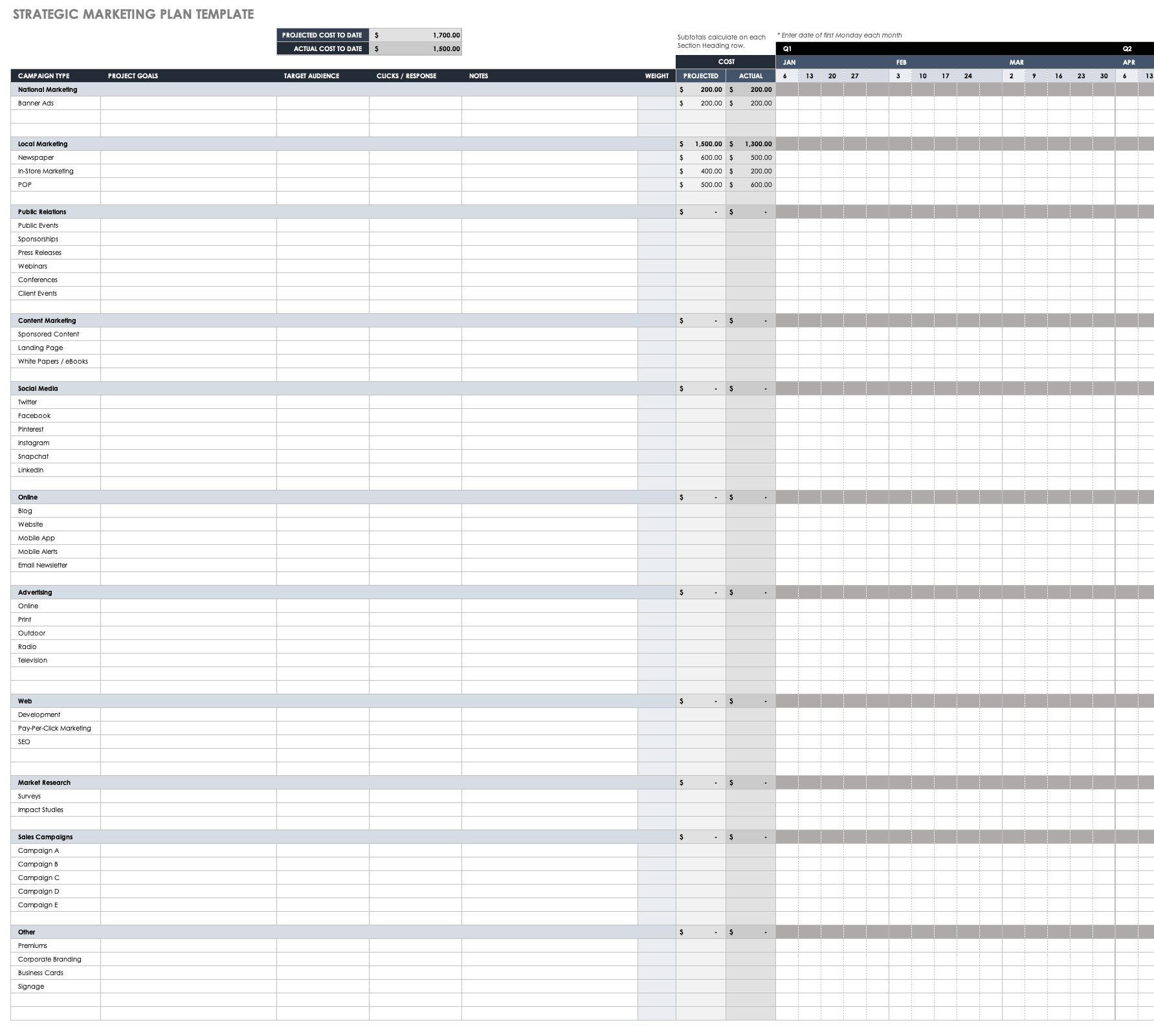
Strategic Marketing Plan Template
Download Strategic Marketing Plan Template
This free strategic marketing plan template includes sections for online marketing campaigns, media relations, trade shows and events, other branding efforts, and sales campaigns. The plan clearly identifies objectives, along with target market and total costs. Months of the year are broken down into weeks for easy planning. You can modify this template to include any elements that are vital to your marketing plan.
Sales & Marketing Plan Template
Download Sales & Marketing Plan Template
This sales and marketing plan template facilitates planning around sales goals and promotional activities. This is an annual marketing calendar template that shows all 12 months on one worksheet. There are sections for public relations, online content marketing, advertising, and research. Monthly sales goals are defined at the top of the template, and there is space at the bottom for metrics to evaluate marketing effectiveness.
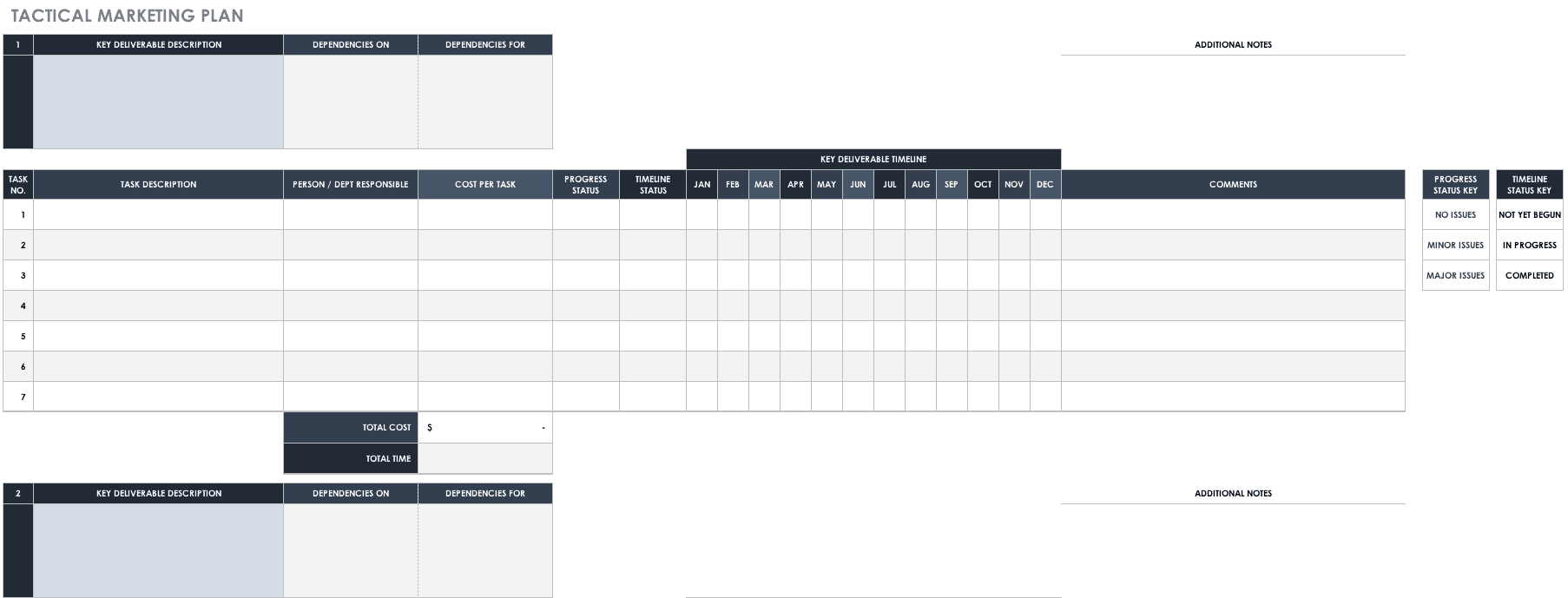
Tactical Marketing Plan Template
Download Tactical Marketing Plan Template
Keep track of the tactics that need to be completed as you implement your marketing strategy. This tactical marketing plan lists each task, the person responsible for the action, expenses, dates, and status. Use this template to keep your plan on schedule and to assess progress.
Product Marketing Plan Template
Download Product Marketing Plan Template
Excel | PDF | Google Sheets
This pre-built product marketing plan template enables you to differentiate your product offering from the competitors by homing in on your unique selling proposition. This template has space to detail the company’s vision, conduct a competitive analysis, define the target market, and establish the market position to ensure your marketing goals stay aligned with the company’s objectives.
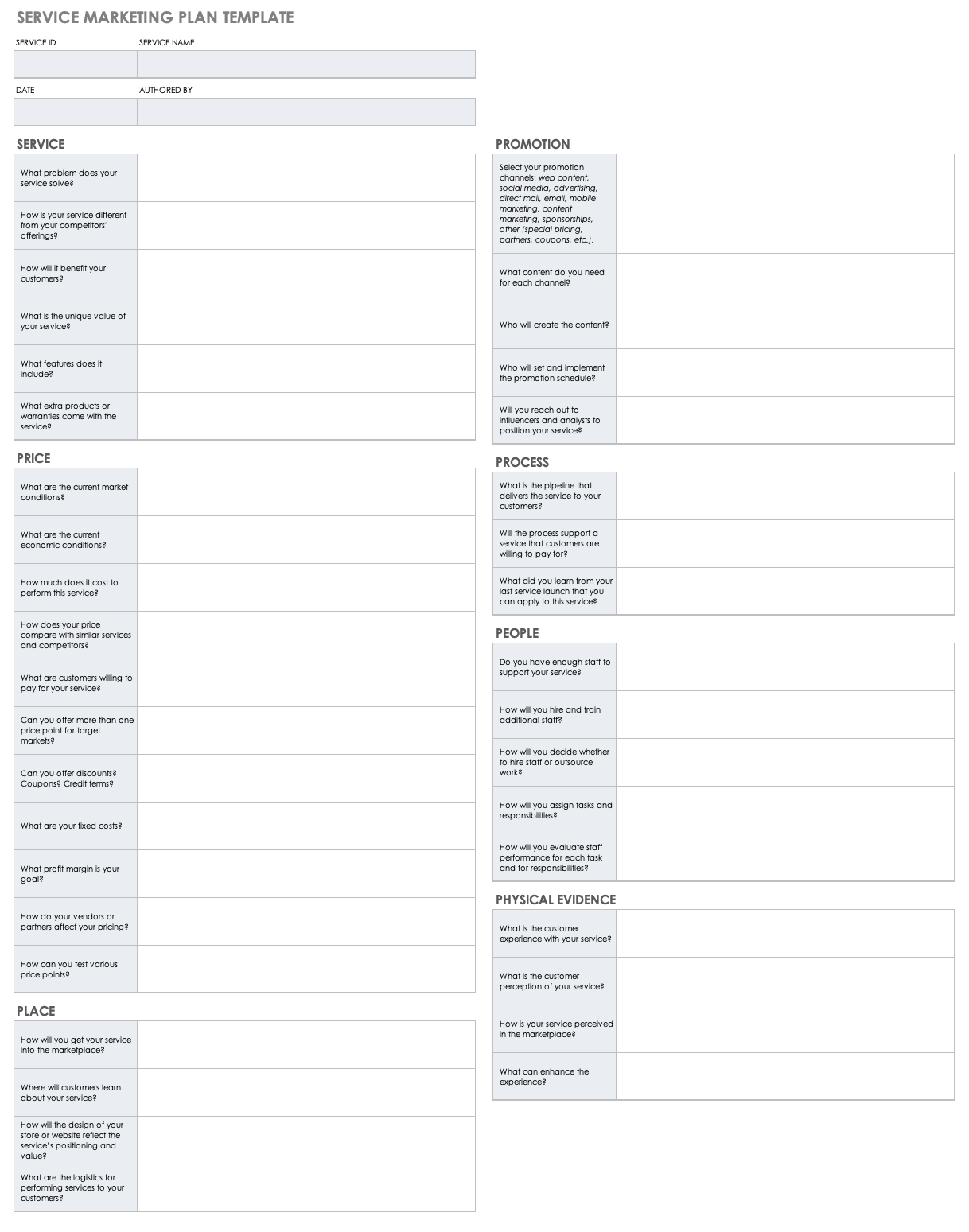
Service Marketing Plan Template
Download Service Marketing Plan Template
Excel | PDF | Google Sheets
Use this customizable service marketing plan template to clearly define your goals and initiatives, analyze your competitors, and outline the characteristics and preferences of your target persona. With space to detail your company’s vision at the top of the template, you can ensure your marketing strategy and initiatives support the mission and values of your company.
What Is a Marketing Plan?
A marketing plan is a document that outlines your marketing strategy. It serves as a roadmap for how your organization aims to raise awareness about a product or service and how it plans to deliver that product or service to target customers. The fundamental purpose of a marketing plan is to align marketing goals with overall business objectives to aid marketing project managers in improving the success of your business or organization.
What your marketing plan looks like will depend on the size and type of your business, but even small businesses and nonprofits can benefit from careful planning.
How to Write a Marketing Plan (and What’s Included)
In this section, you’ll find a comprehensive guide for creating a marketing plan, including an example of a marketing plan outline and links to pages containing free strategic marketing templates.
Pro tip: Save time by using one of the free marketing templates above as a start.
Step 1: Build Your Marketing Plan Outline
A marketing plan outline allows you to structure your plan in a way that makes sense with the product or service you are delivering, and can also serve as a table of contents for your finalized plan. Whether you are a business-to-consumer (B2C) or business-to-business (B2B) company, a small business, or a large enterprise, the details of your plan will vary based on the nature of your business and relative marketing position.
Below, you’ll find an example of a basic marketing plan outline that you can modify to suit your organization’s needs:
-
Title Page
-
Table of Contents
-
Executive Summary
-
Mission and Vision Statement
-
Situational Analysis
-
5C Analysis
-
SWOT Analysis
-
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
-
-
Core Capabilities
-
Goals
-
Business
-
Sales
-
Financial
-
Marketing
-
-
Target Market
-
Audience Persona
-
Information Collection
-
Pain Points and Solutions
-
-
Marketing Strategy
-
Buyers’ Buying Cycle
-
Unique Selling Proposition
-
Branding
-
4Ps
-
Product
-
Place
-
Price
-
Promotion
-
-
Marketing Channels
-
Budgets
-
-
Standards of Performance and Measurement Methods
-
Performance Standards
-
Benchmarks
-
Marketing Metrics
-
Measurement Methods
-
Schedules
-
-
Financial Summary
-
Financial Forecasts
-
Breakeven Analysis
-
Assumptions
-
-
Appendix
-
Research Results
-
Product Specs and Images
-
Step 2: Write Your Mission and Vision Statement
A mission statement is a brief summary of your company’s main purpose, and how your company provides value to its customers. In other words, it should convey your company’s reason for existence, and serve as a point of reference for future planning initiatives. Get started on developing your mission statement by using a free mission statement worksheet.
A vision statement details the future aspirations of a company or entity, and should serve as a framework for short-term and long-term strategic planning. The purpose of a vision statement is to guide internal decision-making for future courses of action. Create a compelling vision statement by using a free vision statement worksheet.
Step 3: Perform a Situational Analysis
Your marketing strategy will not be as effective without a clear picture of the overall health of your business. Gaining deeper insight into your organization’s internal and external environment will allow you to develop a plan that capitalizes on opportunities and reduces risk, and enables you to position your business in the market in a way that sets you apart from competitors.
Three methods you can use to analyze the elements that impact the health of your business are a SWOT analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, and 5C Analysis.
SWOT Analysis
This method is one of the most commonly used tools for analyzing the internal strengths and weaknesses of a business, as well as the external opportunities and threats. When detailing the internal strengths and weaknesses of a business, keep in mind that these are the factors that your company has control over. By contrast, when defining external opportunities and threats, recognize that these are factors that impact your business from the outside, and that you cannot control.
The main purpose of the of a SWOT analysis is to identify weaknesses that can be turned into strengths, and then to leverage strengths in order to take advantage of opportunities and mitigate threats in the market. Choose from a variety of free SWOT Analysis templates, including a SWOT Competitor Analysis template to see how you measure up to competitors.
Porter’s 5 Forces
This framework is used to evaluate your competitive landscape and to identify factors in your industry that may strengthen or weaken your position. The five forces include the following components:
- Industry Rivalry
- Threat of New Entrants
- Bargaining Power of Buyers
- Threat of Substitute Products
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Once you have assessed each of the five forces and rated them from low to high, you will be better equipped to pinpoint and enhance your organization’s competitive position within the industry.
5C Analysis
This marketing framework is used to assess the five key drivers of marketing decisions for a business. The five Cs of the marketing mix include the following:
- Company: Identify the unique value proposition (UVP), or the sustainable competitive advantage that the focal business possesses. Some examples include economies of scale, cost leadership, and differentiation. This component of the assessment involves evaluating the products, services, culture, and brand perception of the business to determine if it’s in the best position to satisfy customer needs.
- Customers: Having keen insight into who your customers are and what motivates them to purchase is essential before determining how you will meet their needs. Conduct research on who is buying your products, how customers interact with your business (including online), seasonal trends, and customer feedback to gain an understanding of the behaviors and preferences of your customer base.
- Competitors: Analyzing your competitors and learning about how they conduct business will enable you to strategize a plan that will beat them at their own game. Learn about your competitor’s strengths, weaknesses, and market position by researching what differentiates them, what kind of content they’re producing, and how their customers interact with and review them.
- Collaborators: Leveraging relationships with people, partners, and distributors that support your daily business operations is key. Since you rely on these collaborators in order to get your product in front of customers, they can be highly beneficial for helping your business run more efficiently. Create a list of all the key players that your business works with — from investors and stakeholders to shippers and photographers — to create strong relations and uncover opportunities.
- Climate: Getting a sense of societal, legal, and industry trends that could affect your business will allow you to make decisions proactively. Get an idea of where the market is heading by keeping a watchful eye on social and economic trends that could impact the way customers are buying, or new technologies like social media that could change the way businesses operate.
Performing a situational analysis by utilizing these methods will allow you to critically analyze your organization and industry landscape, identify opportunities, establish goals, and create a plan of action to take steps toward achieving those goals.
Step 4: Pinpoint Your Organization’s Core Capabilities
Once you’ve conducted your situational analysis and have a clear understanding of the internal and external factors impacting your business, identify the core capabilities of your organization that you can capitalize on to gain a competitive foothold.
One way to home in on your core competencies is to gather feedback from your team by asking the following questions:
- What are our greatest strengths as a company?
- What are our greatest strengths as a team?
- What makes our product offerings better than that of our competitors?
- What makes us the best in our industry?
Your core competencies should be a reflection of your mission and vision statement, and these statements should be modified as core competencies change.
Step 5: Define Your Goals
Are you trying to raise brand awareness? Meet a sales quota? Achieve growth within a specific timeframe? Whatever your primary business, financial, or marketing goals may be, you must ensure they are detailed and data-driven, and that you have the resources needed to achieve them. In other words, you need to establish S.M.A.R.T. goals, which are defined as the following:
- Specific: Clearly convey the main goals you are trying to accomplish.
- Measurable: Determine key metrics you will use to track progress.
- Achievable: Ensure you have the capabilities and resources needed to reach your goals.
- Relevant: Verify that the marketing goals support the overall mission and vision of the business.
- Time-Oriented: Set milestones and deadlines for goals to stay on track.
If you’re feeling uncertain about the main goals you are trying to achieve, here are some questions you can ask yourself to get started on developing them:
- How do we want potential customers to feel about our brand?
- What key elements of our product or service should potential customers know about?
- What will motivate potential customers to choose us over our competitors?
- How is our business positioned in the industry?
- What is our year-to-date (YTD) growth?
- How can we best align our marketing plan with our overall business objectives so they support each other?
Once you’ve answered the above questions, develop and track your S.M.A.R.T. goals by downloading a free goal planning and tracking template.
Step 6: Identify Your Target Market
Once you’ve identified your main goals, the next step is to identify target customers that your business will direct its marketing resources to in order to achieve those goals. Since it isn’t efficient or practical to target everyone, the idea is to focus in on customers that are more likely to choose you over competitors, and to stay loyal to your brand. Read below for tips to help you define your target market.
- Look at the customers you already have: Find out who is already buying your products, and look for mutual interests, preferences, and pain points among those buyers to build customer profiles. Dive in deeper on returning customers, and those that are bringing in the most business, so you can strategize ways to target more buyers with shared characteristics. Another effective way to gain insight into your customer base is to collect information from them by way of focus groups, surveys, research, or simply asking for feedback.
Learn more about customer profiles, and use a free customer profile questionnaire template to get started. - Look at the customers your competitors have: Learn about the customers your competitors are targeting, and figure out what motivates them to choose the competition’s products over yours. Use this information to find niche markets or opportunities your competitor may be missing out on.
- Examine your products and services: Take each product or service offering and list out the key benefits they provide, and then detail how each of those benefits solve a specific problem. Use that information to identify who is most likely to have the problem those benefits provide a solution for, and then create a list of those people.
- Create a target persona: Once you’ve identified the types of people who will most likely benefit from your product, you’ll need to home in on those that are also more likely to purchase it — and choose your brand over the competition. Figure out what the demographics of each buyer looks like (e.g. age, gender, occupation), as well as the characteristics of said buyer (e.g. personality, preferences, lifestyle). Then, identify how your target persona will find your product, what will motivate them to buy it, how they will use it, and how it fits in with his or her lifestyle.
Learn more about target personas, and download a free persona worksheet template to get started.
Step 7: Develop Your Marketing Strategy
Once you’ve established who you are targeting, you need to create a plan for how you will reach them and ultimately convert them into a customer. Ask yourself how you will get in front of your target audience to bring awareness to your product, and how you will convince them to purchase from you. Read below for effective concepts you can use to develop your strategy.
Identify your buyer’s buying cycle.
Now that you’ve pinpointed your target buyer, the next step is to develop a content strategy to encourage the buyer through each stage of the customer’s journey. Understanding how your customers make purchase decisions will allow you to align your content strategy accordingly. The stages of the customer’s buying cycle include the following:
- Awareness: Prospective buyers have a problem and begin searching for solutions. This is the stage where a business invests its resources to make potential customers aware of the products and services it offers.
- Consideration: Prospective buyers are considering the various solutions available to solve their problem, and need to be convinced that they need to make a purchase in order to solve it. This is the stage where a business conveys in great detail the benefits the customer will receive after using the product, and how it is better than what the competition is offering.
- Intent: Prospective buyers are convinced that they need to make a purchase to solve their problem, and begin to compare alternatives. This is the stage where a business reassures the customer that the product offered makes the most sense out of all the alternatives from an emotional, financial, or lifestyle perspective.
- Purchase: Prospective buyers have made their decision on which company they will purchase the product from. Even if the buyer chooses your product, the process does not end here. The goal of your business is to develop a relationship with the customer to increase brand loyalty, and to find upsell opportunities based on purchase history.
- Repurchase: Buyers need to renew a perishable product (e.g. a supply of contact lenses) or a product subscription. The goal of your business is to foster the relationship with the customer by offering incentives to repurchase and to increase brand evangelism. An effective way to use content to retain customers is through email marketing campaigns. Find email workflow tips, examples and free templates to get started on developing your strategy.
Before creating content for each stage of the buying cycle, you must first establish your content goals for each stage, strategies to implement to meet those objectives, and the key metrics to measure results.
Develop your content strategy for each phase of the cycle and choose from a wide variety of free content marketing templates.
Determine the 4Ps of your marketing mix.
In order to effectively guide potential customers through each phase of the buyer’s lifecycle, use your marketing project management skills to create a strategy to get your brand in front of them, and then motivate them to purchase your product. As you develop your strategy, refer to the following 4Ps of your marketing mix:
- Product: This refers to the tangible good (or intangible service) that you are offering as a solution to meet the needs of the customer. Emphasizing the UVP and differentiating your product in the market are the first steps to setting yourself apart and positioning your brand.
- Price: This refers to the price your customer is expected to pay for the product. Understanding the perceived value (e.g. high quality versus low quality) of your product in the eyes of the customer is imperative before you can effectively set a price. Researching the price competitors are offering for similar products or alternatives is a great place to start.
- Promotion: This refers to the communication aspect of your marketing strategy. Getting the word out about your product is the best way to raise awareness about your brand, with methods including press releases, trade shows, event marketing, videos, and advertising.
- Place: This refers to the place where customers can purchase your product. Will you sell exclusively online? Will customers need to come to a physical location? The marketing channels you will use to get the product from producer to customer (e.g. direct selling, mail order, online) are a part of your distribution strategy.
According to Justin Mares and Gabriel Weinberg, authors of the book Traction: How Any Startup Can Achieve Explosive Customer Growth, some key marketing channels to use to raise awareness about your brand include the following:
- Relevant blogs
- Publicity
- Unconventional PR
- SEM/SEO
- Paid Ads/Remarketing
- Offline Ads
- Content Marketing
- Email Marketing
- Trade Shows
- Speaking Engagements
- Marketing Events
- Community Events
Create your budget.
Setting a budget will give you parameters to work within as you are implementing your plan. It also enables you to prioritize your needs before your wants so you can dictate resources (e.g. talent acquired) toward high priority goals first. Here are some helpful tips you can use to create your marketing budget:
- Build your budget plan based on last year’s numbers, or build from scratch according to priority.
- Make a list of action items, and then come up with an estimated budget for each item based on marketing, distribution, and promotional expenses.
- Prioritize your needs before your wants. Whatever is leftover after your needs are fulfilled, funnel those funds toward your wants.
- Invest in areas with higher return on investment (ROI) (e.g., content marketing, email marketing) to increase your buying power.
Find a wide range of free marketing budget templates to start planning your budget.
Step 8: Create a Value-Complexity Matrix
Once you have established your marketing tactics and set out a budget to work within, you’ll need to prioritize your plan of attack by going after low hanging fruit. In other words, you need to act on the high value items that don’t require as much effort to complete, or the “easy wins.”
Take each initiative and assign it to a quadrant within the following matrix to determine if the time and resources needed to complete the initiative are worth the value it will return.
Step 9: Conduct Financial Projections
This segment of the plan shows the financial projections you have determined to be relevant to the project based on the research you have completed for your marketing plan. This component of the marketing plan is critical in order to gain buy-in from stakeholders and investors, and to guide your decisions throughout the duration of the project.
Common financial data to add to your marketing plan include the following:
-
Forecasts (sales and expenses)
-
Break even analysis
-
Financial requirements
-
3 year financial projections
-
Income statement
-
Cash flow statement
-
Balance sheet
-
Find a free sales forecast template, financial projections template, and other templates to prepare your financial data by checking out this page with free startup plan, budget and cost templates.
Step 10: Identify Standards of Performance and Results Tracking Methods
The primary purpose of setting performance standards is to communicate clear expectations and desired results for an organization’s marketing efforts. For example, a performance standard might be that the total budget for X will equal a specific percentage of the yearly promotional budget for the coming year.
Before you can adequately measure the outcome of marketing initiatives, there are some steps you must take to lay the groundwork.
- Determine your key performance indicators (KPIs): Define measurable marketing metrics and connect them to your established goals in order to track progress.
- Establish a baseline: Understand and document how your business is currently performing so you have something to compare future performance results to.
- Define your benchmarks: Acquire data about your competition and industry to develop standard measurements that indicate how you stack up against the competition.
- Decide which tools and platforms to implement: The results you analyze are only as good as the methods you use to track them. Find a project management platform that provides real-time visibility into project status and performance so you have the ability to make timely, data-driven decisions.
Once you’ve completed these steps, you can begin the process of tracking performance by doing the following:
- Establish guidelines on results tracking (e.g. what to track and how often), and determine who is responsible.
- Schedule meetings to evaluate results and determine where opportunities lie. Come to each meeting prepared by using a free meeting agenda template.
- Take inventory of your content and compile a list of the top performers. Compare the results of that content to your standards of performance to see if they align, and to identify what can be improved upon. In this article, you can choose from 60-plus content marketing templates, including a content inventory template, to help you plan and execute your content marketing strategy.
- When performance improves, identify what contributed to it and allocate resources accordingly.
Once you’ve identified the standards to use to measure the effectiveness of your marketing strategy, the next course of action is to implement your plan, measure performance, and adjust accordingly.
Step 11: Write the Executive Summary
Although the executive summary is placed at the beginning of your marketing plan, it is the final step to be completed. This section summarizes all the key takeaways from each segment of the marketing plan, and should ultimately answer each of the following questions:
- What are the overall business objectives?
- How do your marketing goals align with the business objectives?
- Which products or services will you market?
- Who is your target audience?
- What resources will you leverage (e.g. partnerships) to get your products in front of prospects?
- What gives you a competitive advantage?
- What problems are you solving?
- What solutions are you providing?
- What are the short and long-term goals of the company?
Learn more about how to create an effective summary, and find free checklists and templates to support your efforts by visiting “How to Write an Effective Executive Summary to Yield Results.”
It’s important to remember that a marketing plan is not static, but rather a living document that should be referenced regularly, and updated as changes occur within your business and the larger business climate.
Marketing Plan Examples and Samples
In this section, you will find examples of marketing plans created by established companies, along with sample marketing plan, to help guide you in your efforts in creating your own plan.
-
Lush Marketing Plan (provided by Calameo)
This first example is a marketing plan that was created for a cosmetics company. You will note that design elements throughout this plan are consistent to the brand, and sections are broken up by catchy graphics and illustrations.
-
RE/MAX Marketing Plan (provided by Calameo)
This example is a marketing plan that was created for a real estate company. This plan emphasizes the benefits that a customer receives by using their services, and details the promotional strategy used to connect customers to their business.
-
Marketing Plan Sample (provided by Houghton Mifflin Company)
This sample shows a marketing plan for a hypothetical company. Although this plan does not display any design elements or graphs, it breaks the plan up into the key components of a basic marketing plan.
Benefits of a Strong Marketing Strategy and Marketing Plan
A strong marketing plan can serve as a roadmap for your organization, and taking the time to write a formal plan — rather than relying on esoteric goals or vague strategy — can heighten the success of your overall marketing efforts. A marketing plan can help you accomplish the following:
- Pinpoint high priority initiatives.
- Eliminate projects that don’t move you toward your goals.
- Identify the right metrics to track.
- Give your team direction and alignment.
- Set realistic and measurable objectives.
- Answer key questions about your business (and how this effort fits into high-level organizational goals).
- Identify your target audience/customers and define how to best reach them.
- Develop a structured approach to building products and services that satisfy customers’ needs.
- Retain your customers.
- Save time and money.
Ultimately, your marketing plan acts as a reference document that will hold you accountable and help you execute your marketing strategy.
Best Practices for Creating a Strategic Marketing Plan
You can elevate the utility of your marketing plan by taking extra time to add elements and perform in-depth analysis of your audience, brand, and budget. Below are some tactical and analytical tips that will help you get the most out of your marketing strategy planning:
- Create a dynamic marketing plan. With so much information to cover, your plan might end up being a long, text-heavy document. Include a table of contents so that your readers can easily navigate through the plan, use bullet points to break up walls of text, and include visual illustrations that draw the eye. Also consider creating a one-page version that captures the most important high-level information.
- Back up your plan with research. All of the information provided in your plan will be more credible if you can back it up with research and facts before you go to market. Attach an appendix for any supporting material, and provide graphics (tables, graphs, pictures, etc.) to substantiate your statements and analysis.
- Understand your audience. A successful marketing campaign hinges on being able to connect your message with your target market. Use Google Analytics or another engagement analysis platform to identify your audience and their behavior, and consider creating audience personas so that you know who you are producing content for.
- Ensure your brand is strong and stands out. This concept is complex and requires continual attention and iteration. From a marketing perspective, you can begin building brand integrity by defining your unique selling proposition, optimizing and designing your website and all other distribution channels, and creating great content. Be sure to elicit feedback from other departments so that the marketing material is in line with organizational messaging and goals.
- Create realistic financial goals. Like all other business concerns, success relies on sound budgeting. Define your budget early on to set expectations around spending and to identify any potential financial gaps, and create some metrics and KPIs that are related to financial success. In addition, make sure you can realistically support any special offers, discounts, or rewards that you offer.
You can also tap into several accessory activities to strengthen your marketing planning. These include the following:
- Promotions strategies
- Online marketing strategy
- Joint ventures and partnerships
- Referral strategy
- Strategy for increasing transaction prices
- Retention strategy
Design Tips for a Marketing Plan
Presentation is key when it comes to showcasing your marketing plan to potential investors and stakeholders. Below are some basic best practices to keep the look of your plan interesting and streamlined:
- Keep design elements and formatting consistent throughout the design brief and plan.
- Incorporate icons, charts, and infographics to make the plan more visually compelling.
- Use borders and colors (ensure consistency with your branding style guidelines) to section out your marketing plan.
- Emphasize key stats and metrics to make it scannable.
- Create a visual of your target audience persona.
- Use design elements that reflect your high-level marketing goals.
- Use a template to incorporate your own unique touch and branding.
Improve Your Marketing Strategy and Plan with Smartsheet for Marketing
The best marketing teams know the importance of effective campaign management, consistent creative operations, and powerful event logistics -- and Smartsheet helps you deliver on all three so you can be more effective and achieve more.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.